Compact square Photoelectric Sensors
Compact square Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric Sensors
What Is a Photoelectric Sensor?
What Is a Photoelectric Sensor?
Photoelectric Sensors detect objects, changes in surface conditions, and other items through a variety of optical properties.
A Photoelectric Sensor consists primarily of an Emitter for emitting light and a Receiver for receiving light. When emitted light is interrupted or reflected by the sensing object, it changes the amount of light that arrives at the Receiver. The Receiver detects this change and converts it to an electrical output. The light source for the majority of Photoelectric Sensors is infrared or visible light (generally red, or green/blue for identifying colors).
Photoelectric Sensors are classified as shown in the figure below.
Through-beam Sensors
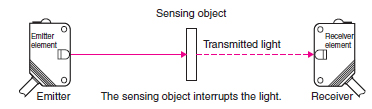
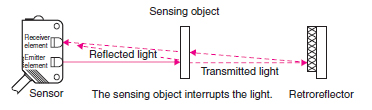
Retro-reflective Sensors
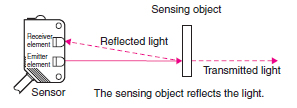
Diffuse-reflective Sensors
Features
1. Long Sensing Distance
A Through-beam Sensor, for example, can detect objects more than 10 m away. This is impossible with magnetic, ultrasonic, or other sensing methods.
2. Virtually No Sensing Object Restrictions
These Sensors operate on the principle that an object interrupts or reflects light, so they are not limited like Proximity Sensors to detecting metal objects. This means they can be used to detect virtually any object, including glass, plastic, wood, and liquid.
3. Fast Response Time
The response time is extremely fast because light travels at high speed and the Sensor performs no mechanical operations because all circuits are comprised of electronic components.
4. High Resolution
The incredibly high resolution achieved with these Sensors derives from advanced design technologies that yielded a very small spot beam and a unique optical system for receiving light. These developments enable detecting very small objects, as well as precise position detection.
5. Non-contact Sensing
There is little chance of damaging sensing objects or Sensors because objects can be detected without physical contact.
This ensures years of Sensor service.
6. Color Identification
The rate at which an object reflects or absorbs light depends on both the wavelength of the emitted light and the color of the object. This property can be used to detect colors.
7. Easy Adjustment
Positioning the beam on an object is simple with models that emit visible light because the beam is visible.
Compact square Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric Sensors
What Is a Photoelectric Sensor?
What Is a Photoelectric Sensor?
Photoelectric Sensors detect objects, changes in surface conditions, and other items through a variety of optical properties.
A Photoelectric Sensor consists primarily of an Emitter for emitting light and a Receiver for receiving light. When emitted light is interrupted or reflected by the sensing object, it changes the amount of light that arrives at the Receiver. The Receiver detects this change and converts it to an electrical output. The light source for the majority of Photoelectric Sensors is infrared or visible light (generally red, or green/blue for identifying colors).
Photoelectric Sensors are classified as shown in the figure below.
Through-beam Sensors

Retro-reflective Sensors

Diffuse-reflective Sensors

Features
1. Long Sensing Distance
A Through-beam Sensor, for example, can detect objects more than 10 m away. This is impossible with magnetic, ultrasonic, or other sensing methods.
2. Virtually No Sensing Object Restrictions
These Sensors operate on the principle that an object interrupts or reflects light, so they are not limited like Proximity Sensors to detecting metal objects. This means they can be used to detect virtually any object, including glass, plastic, wood, and liquid.
3. Fast Response Time
The response time is extremely fast because light travels at high speed and the Sensor performs no mechanical operations because all circuits are comprised of electronic components.
4. High Resolution
The incredibly high resolution achieved with these Sensors derives from advanced design technologies that yielded a very small spot beam and a unique optical system for receiving light. These developments enable detecting very small objects, as well as precise position detection.
5. Non-contact Sensing
There is little chance of damaging sensing objects or Sensors because objects can be detected without physical contact.
This ensures years of Sensor service.
6. Color Identification
The rate at which an object reflects or absorbs light depends on both the wavelength of the emitted light and the color of the object. This property can be used to detect colors.
7. Easy Adjustment
Positioning the beam on an object is simple with models that emit visible light because the beam is visible.












